Core Advantages of Face Recognition Devices: From Efficiency Innovation to Security Enhancement
This article contains AI assisted creative content

Core Advantages of Face Recognition Devices: From Efficiency Innovation to Security Enhancement
In an era where digital transformation and intelligent living are deeply integrated, face recognition devices, leveraging their unique technological features, have evolved from simple identity verification tools into core equipment that drives efficiency improvement, security enhancement, and experience optimization across various industries. Their advantages are not only reflected in technical convenience and accuracy but also deeply penetrate into the practicality, economy, and inclusiveness of scenario-based applications, making them a key force in reshaping modern lifestyles and work patterns.
From the perspective of operational convenience, face recognition devices have completely broken the physical limitations of traditional identity verification methods, enabling efficient "contactless and medium-free" interaction. Traditional verification relies on carriers such as keys, ID cards, and passwords, which suffer from drawbacks like inconvenience to carry, easy loss, and frequent forgetfulness. For instance, employees may be unable to enter the office area due to forgetting their access cards, and users may repeatedly attempt to log in to systems because they mix up passwords. In contrast, face recognition devices automatically capture facial features via cameras. The entire verification process requires no manual intervention, taking only 0.3 to 0.5 seconds from recognition to completion of authentication. Moreover, users do not need to make deliberate efforts to cooperate (unlike fingerprint recognition, which requires pressing, or iris recognition, which requires aligning with the lens). Even couriers holding packages or travelers with luggage can quickly complete identity verification. This "seamless access" experience is particularly advantageous in high-traffic scenarios: after airports adopted face recognition devices, the passenger clearance time was reduced from 20-30 seconds (with traditional manual verification) to less than 5 seconds; after office buildings installed face recognition access control, the waiting time for employees during morning peak hours decreased by 70%, significantly improving daily traffic efficiency.
In terms of security protection capabilities, face recognition devices have built a security barrier far superior to traditional methods through multiple technical means. On one hand, they rely on the uniqueness of biometric features to ensure security. Facial features are determined by both genes and the living environment, possessing irreproducible and irreplaceable characteristics. This avoids risks such as key duplication, password cracking, and ID card forgery. For example, if a traditional access card is accidentally lost, it may be used by others to enter sensitive areas; however, face recognition devices can accurately distinguish between individuals by analyzing dozens of key feature points, such as facial contours, eye spacing, and eyebrow curves—even identical twins can be accurately identified through subtle feature differences. On the other hand, modern face recognition devices generally integrate "liveness detection" technology. Through infrared sensing, 3D depth imaging, and micro-expression capture, they effectively prevent attacks using counterfeit methods such as photos, videos, and 3D-printed masks. Infrared sensors can identify the temperature and texture characteristics of the skin, eliminating deception by paper photos; 3D depth cameras can capture the three-dimensional contours of the face, avoiding forgery by 2D videos; some high-end models can even detect subtle movements like blinking and smiling, further ensuring that the verification object is a real living person. This provides stronger guarantees for scenarios with high security requirements, such as finance and government services.
From the angle of scenario adaptability, face recognition devices have strong environmental compatibility and functional expandability, allowing them to flexibly meet the diverse needs of different industries. In terms of environmental tolerance, through hardware optimization and algorithm adjustment, they can cope with complex lighting, temperature, and occlusion conditions. In low-light environments, the infrared fill-light module can be automatically activated to ensure clear facial capture even in darkness; in backlit scenarios, Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) technology can balance the brightness of bright and dark areas, preventing facial blurriness caused by strong light; for occlusion situations such as wearing masks, glasses, or hats, the algorithm can focus on unobstructed feature points (e.g., eyes, forehead) to achieve accurate recognition. This advantage was particularly important during the pandemic, when mask-wearing was generally required in public places. Face recognition devices, through the "mask mode," still maintained a recognition accuracy of over 95%, ensuring the normal operation of scenarios such as access control and payment. In terms of functional expansion, face recognition devices can seamlessly connect with other systems to generate rich application value: in retail scenarios, they can identify repeat customers by combining consumption data and automatically push personalized promotions; in campuses, they can link with attendance systems to record students' arrival and departure times in real time and synchronously notify parents; in communities, they can connect with security cameras, and once a stranger is identified loitering, they immediately send an early warning to property management, realizing the dual functions of "identity verification + security monitoring."
The exploration of management efficiency and data value is another core advantage that face recognition devices bring to enterprises and institutions. Traditional identity verification methods rely on manual management, which not only incurs high costs but also is prone to problems such as data confusion and human errors. For example, when manually registering visitor information, records may be incorrect due to illegible handwriting, or security risks may arise from missed registrations; when factories manually count employee attendance, it takes a lot of time to verify clock-in records, and it is difficult to prevent proxy clock-ins. In contrast, face recognition devices can realize full-process automated management: in visitor management, visitors only need to take a facial photo on-site and register information, and the system automatically generates temporary permissions and cancels them when the visitor leaves—no manual registration or credential recovery is required; in attendance management, employees automatically complete clock-in when entering or exiting, and data is synchronized to the cloud system in real time. Administrators can directly export attendance reports through the background, eliminating proxy clock-ins and saving more than 80% of the time spent on attendance statistics. More importantly, the identity data accumulated by face recognition devices can be transformed into valuable operational references: shopping malls can accurately count peak passenger flow and the age and gender distribution of customers by analyzing visitor facial data at different times, thereby optimizing store layout and promotion schedules; enterprises can reasonably adjust work schedules and workstation resources by analyzing the time patterns of employees entering and exiting the office area, improving space utilization efficiency.
In terms of cost-effectiveness, the long-term benefits of face recognition devices far exceed the initial investment, bringing significant cost savings to users. In the short term, although they require a certain amount of equipment purchase and installation costs, they can eliminate the ongoing consumption of traditional verification methods. For example, enterprises no longer need to produce and reissue access cards for employees (each card costs 10-20 yuan, and for an enterprise with 1,000 employees, the annual reissue cost can reach tens of thousands of yuan); residential communities do not need to hire special personnel to manage access registration, saving tens of thousands of yuan in labor costs annually. In the long term, the low maintenance requirement of face recognition devices further reduces costs: their core components (such as cameras and AI chips) have a service life of 5-8 years, and there is no need for frequent replacement of consumables (unlike fingerprint scanners, which require regular replacement of fingerprint collection films); system upgrades can be completed through remote pushes, without on-site disassembly and debugging, reducing the cost of dispatching maintenance personnel. In addition, face recognition devices can indirectly reduce economic losses caused by security incidents: for example, after warehouses adopt face recognition devices, they can avoid goods theft caused by the fraudulent use of access cards, reducing property losses of hundreds of thousands of yuan; hospitals can prevent medical disputes caused by identity confusion by verifying patients' identities through face recognition, lowering compensation costs.
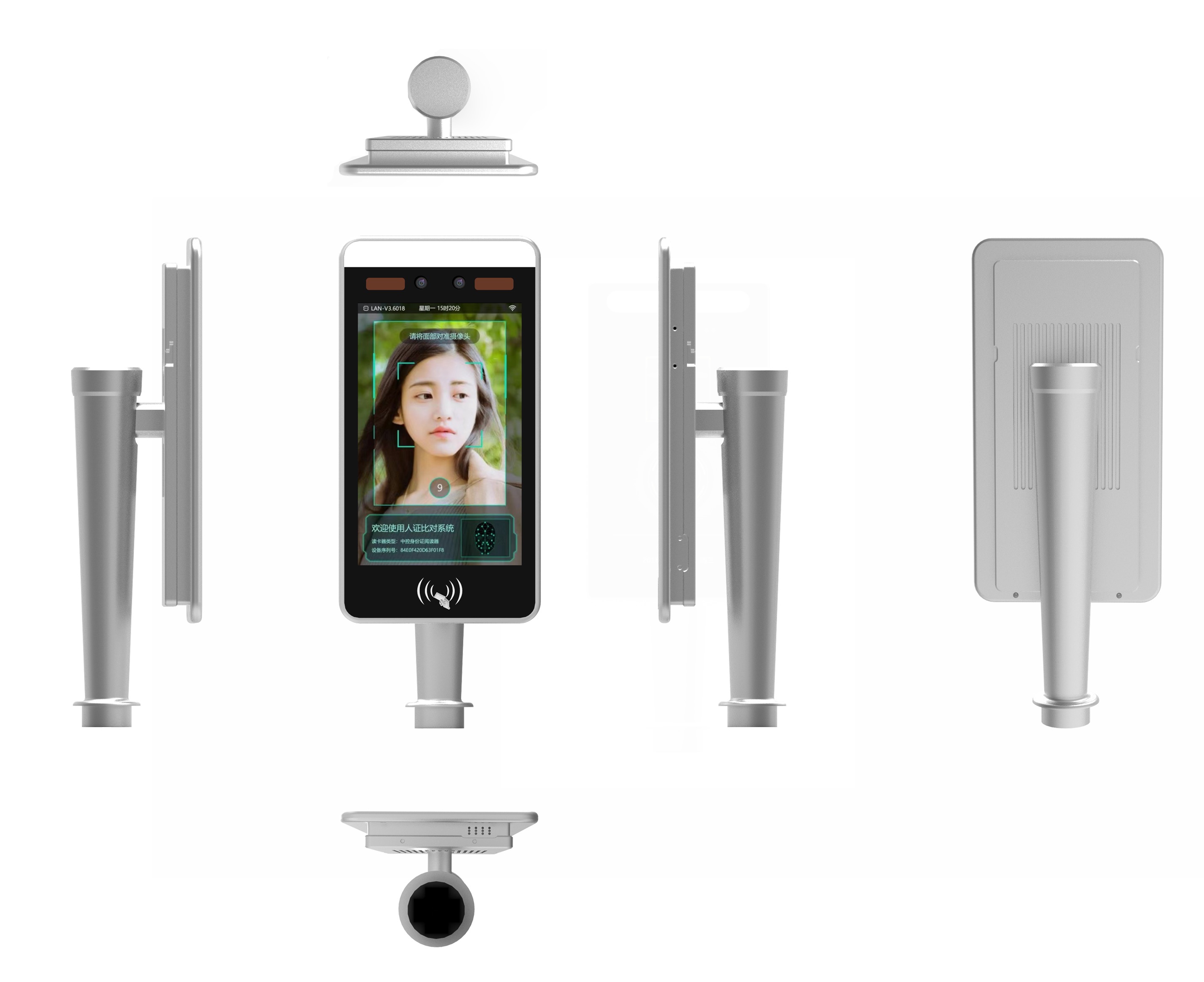

In terms of social inclusiveness, face recognition devices have broken the limitations of age and physical conditions, allowing more people to conveniently enjoy intelligent services. Traditional verification methods are not user-friendly for special groups: the elderly may be unable to enter passwords accurately due to degraded eyesight, and people with disabilities may find it difficult to use fingerprint scanners due to hand function impairments. In contrast, face recognition devices do not require users to have specific operational capabilities. The elderly only need to face the camera naturally to complete verification, and people with physical disabilities do not need to touch the device with their hands, truly realizing "zero-threshold" use. In government service scenarios, some local government service halls have installed face recognition devices. When the elderly handle social security and medical insurance services, they do not need to carry ID cards or social security cards—they can quickly retrieve personal information through facial verification, avoiding multiple trips due to forgotten documents; in public transportation scenarios, face recognition turnstiles support "face-swiping for rides," eliminating the need for users to prepare transit cards or mobile phones in advance, providing great convenience for passengers with limited mobility and reflecting the humanistic care of technology.
From the perspective of technological prospects, face recognition devices have the potential to integrate with cutting-edge technologies, reserving space for future intelligent development. With the continuous advancement of the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and 5G technologies, face recognition devices can serve as "intelligent entry points" to connect more intelligent devices and build an integrated ecosystem. In smart homes, after identifying the user's identity, face recognition devices can automatically link with devices such as lights, air conditioners, and curtains to adjust to the user's preferred mode (e.g., when a child is identified returning home, the child mode is automatically activated, reducing light brightness and locking dangerous areas); in industrial scenarios, they can connect with production equipment and monitoring systems—only when the face of an authorized employee is verified can precision instruments be started, and the operation process can be monitored in real time to ensure production safety; in smart cities, face recognition devices can be integrated into the public security network to assist in public security prevention and control by identifying suspicious persons, or quickly confirm the identity of missing persons in emergency situations, improving urban governance efficiency. This technological extensibility enables face recognition devices not only to meet current needs but also to adapt to the intelligent upgrade requirements of the next decade or even longer.
In summary, the advantages of face recognition devices are multi-dimensional and in-depth: they not only solve the efficiency pain points and security risks of traditional identity verification methods but also provide data-driven management ideas for various industries, and cover a wide range of people with their economical and inclusive characteristics. From airports and banks to communities and campuses, from daily travel to financial transactions, face recognition devices are reshaping the logic of identity verification with their unique value, becoming an important bridge connecting people and the intelligent world, and promoting society toward a more efficient, secure, and convenient direction.












Please first Loginlater ~